Curriculum
- Art
- Computer Science
- Drama
- English
- Food Technology
- Geography
- History
- Maths
- Modern Foreign Languages
- Music
- PSHE
- Physical Education
- Psychology
- Religious Studies
- Science
- Technology
- Exams
- Exam Results
- GCSE Subjects
- Extra-Curricular Clubs and Enrichment Activities
- Careers
- Attitude to Learning Descriptors
- Special Educational Needs
- Go 4 Schools Parent/Carer User Guide
Curriculum Intent
Technology holds a unique place within the school curriculum, it is the subject of the man-made world around us and how we interact with it, and so one of the major strengths of all the subject specialisms taught within Technology lie in their ability to help students to identify potential improvements to current products and processes, and so empower them to try to improve current products and change the world around themselves for the better.
Technology as a subject is both intellectual and practical in nature. Through testing, experimentation and manufacturing products students develop a practical knowledge of the working properties of materials as well as knowledge of both hand and computer aided manufacturing techniques; they develop both hand and computer aided design drawing and presentation skills; and use ICT to help research, communicate and realise their ideas. These skills are backed up by an intellectual understanding of the design process and design history, as well as imaginative problem solving, analytical and evaluative skills that will enable students to produce well-designed products that meet the needs of the target market. Students are also introduced to the possibilities presented by new and emerging technologies such as smart materials and they also consider the social, moral and environmental impact on society of design and future technological developments.
As well as providing students with the opportunity to explore their creativity, build on previous skills and knowledge and develop a high standard of presentation as designers are required to do in the real world the curriculum has been designed to re-enforce the close links between Technology and not just Maths and Science, but to Computer Science, Art & Design, Humanities, Physical Education and be seen as a subject that links the wider school curriculum.
Key Stage 3
As students often arrive in secondary education without little or no Technology experience at KS2 students are introduce to Health & Safety in the workshop and are guided in good practice in practical work. Investigations are carried out into physical properties and manipulation techniques of common woods, metals, plastics, papers, cards, boards and natural and synthetic compliant materials. Pupils are introduced to CAD/CAM, systems and control along with joining materials. The origin sources of materials, and issues surrounding sustainability are explored. The design process is introduced and followed throughout student rotations, this encourages students to critically evaluate their designs and products and suggest modifications and improvements. Students are introduced to current and historical key designers, their iconic brands and products and the reasons for their success. Subjects currently studied at KS3 are – Resistant Materials, Graphics and Food.
Key Stage 4
(Food is a separate subject at KS4, please see the Food website page for more information)-:
Learning in TECHNOLOGY is broken down into three main components:
Core Technical Principles:
Students explore new and emerging technologies, energy storage, developments in new materials, mechanical devices, core materials and their properties.
Specialist Technical Principles:
As a part of the designing and making processes students are exposed to schemes covering selection of materials, forces and stresses, ecological footprints, sources and origins of materials, stock, forms, sizes and types, scales of production and their implementations, specialist techniques and surface treatments/finishes.
Designing & Making Principles:
Students are guided through the design process and are aware for the need for research, designing, developing, realising and evaluating, and appreciating that the approach can be holistic.
Aims and outcomes
- Students will be able to demonstrate their understanding that all design and technological activity takes place within contexts that influence the outcomes of design practice
- Students will aim to develop realistic design proposals as a result of the exploration of design opportunities and users’ needs, wants and values
- Students will use imagination, experimentation and combine ideas when designing.
- Students will develop the skills to critique and refine their own ideas whilst designing and making.
- Students should be able to communicate their design ideas and decisions using different media and techniques, as appropriate for different audiences at key points in their designing.
- Students will develop decision making skills, including the planning and organisation of time and resources when managing their own project work
- Students will develop a broad knowledge of materials, components and technologies and practical skills to develop high quality, imaginative and functional prototypes.
- Students should be encouraged to be ambitious and open to explore and take design risks in order to stretch the development of design proposals, avoiding clichéd or stereotypical responses
- Students should consider the costs, commercial viability and marketing of products.
- Students must demonstrate safe working practices in design and technology
- Students must use key design and technology terminology including those related to: designing, innovation and communication; materials and technologies; making, manufacture and production; critiquing, values and ethics.
Subjects specialisms studied at KS4 are – Resistant Materials and Graphics
Exam board
We follow the AQA exam board. This is the link to the specification (Food is a separate subject at KS4, please see the Food page on the website for more information)-:
https://www.aqa.org.uk/subjects/design-and-technology/gcse/design-and-technology-8552
Curriculum Implementation
KS3 Technology students their year is split in studying Resistant Materials, Graphics and Food Technology. Students complete a 22 lesson ‘course’ in each subject area before moving on to the next subject to ensure that all students get a chance to study each subject during the year. At the end of the year students revisit all subject areas for a second time for a series of 2 week ‘mini-projects’.
The current KS3 Project breakdown is as follows-
|
Year 7 Resistant Materials |
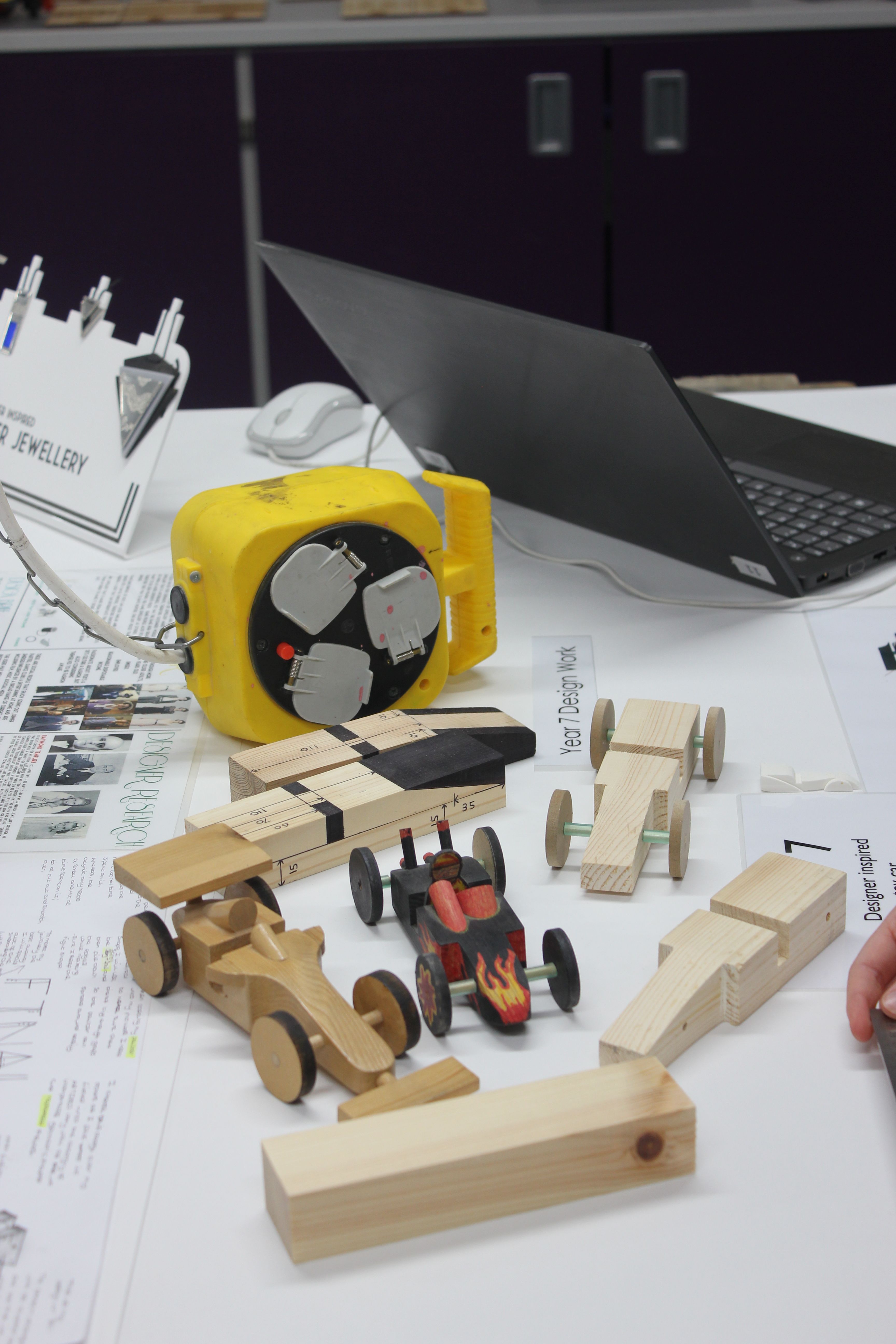
Designer influenced toy car project |
|
Year 7 Graphics |
Biomimicry design project, technical drawing skills |
|
Year 7 Food |
H&S, knife skills and Queen cake technical challenge |
|
Year 8 Resistant Materials |
Art Deco pewter jewellery project |
|
Year 8 Graphics |
App Icon design project, Photoshop movie promotional artwork project, Bottle label project. |
|
Year 8 Food |
Design and Make project - Bread |
|
Year 9 Resistant Materials |
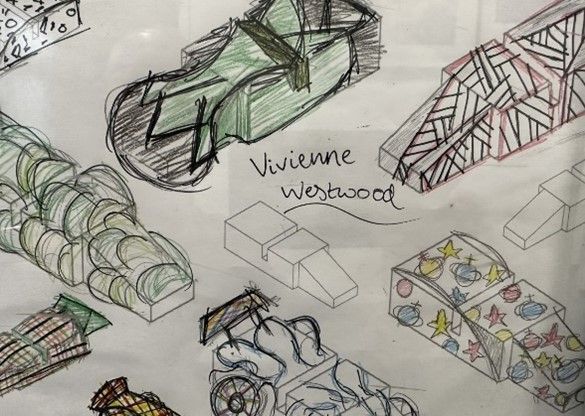
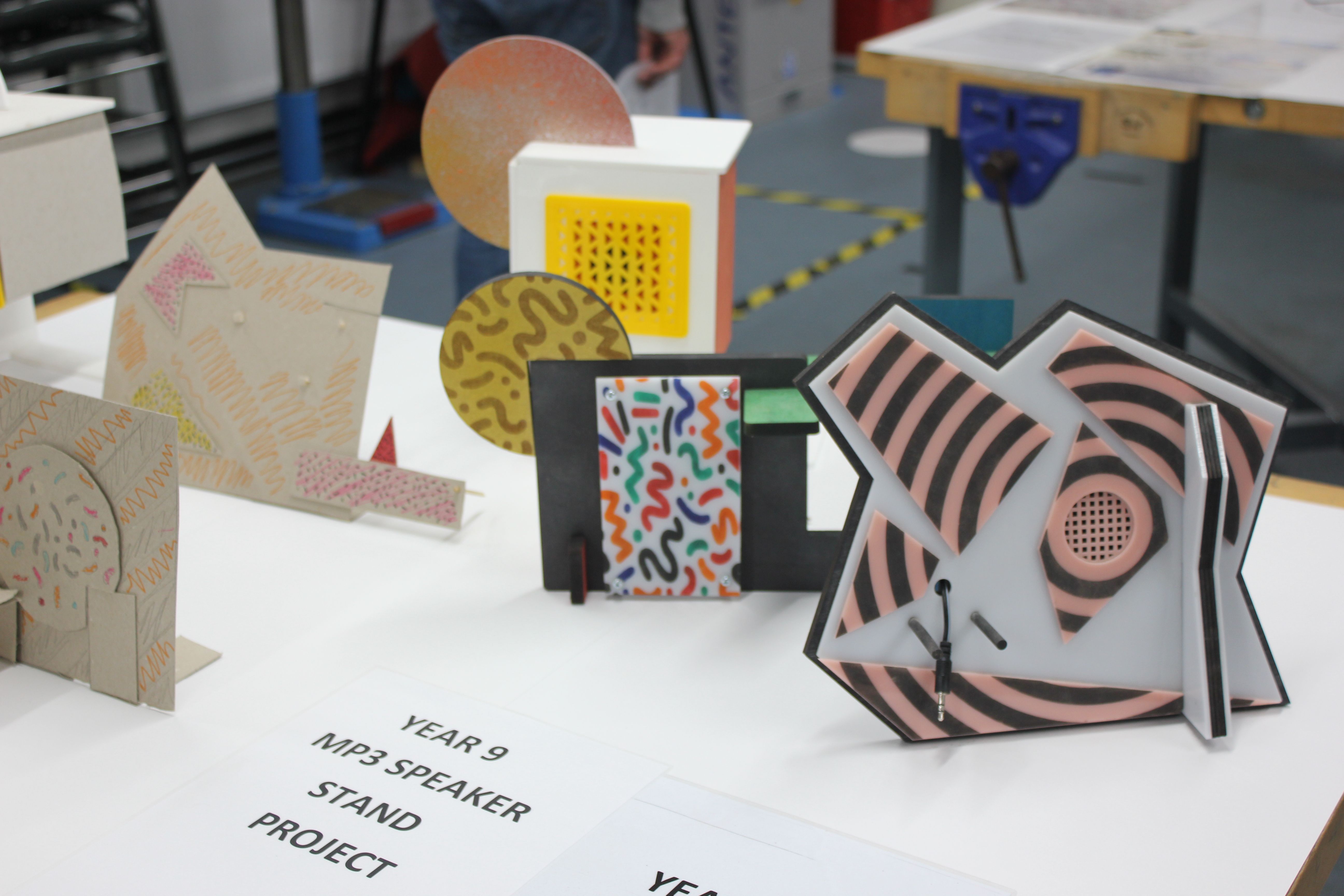
Memphis design inspired MP3 speaker project. |
|
Year 9 Graphics |
Grand Designs architectural modelling project. |
|
Year 9 Food |
Multi-cultural foods project. |
The current KS4 Technology breakdown is as follows (Food is a separate subject at KS4, please see the Food page on the website for more information)-
|
Year 10 Graphics and Resistant Materials |
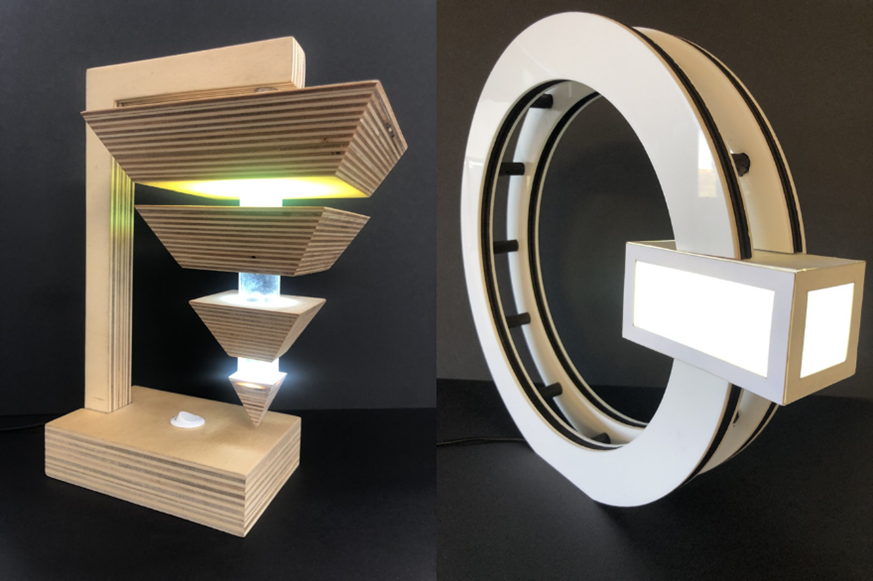
Students start with a 10 lesson practical project to build on the skills they learnt in KS3. Students then move on to a lighting design project. This project is structured and assessed in exactly the same way that their GCSE non-exam assessment project will be. This project is interspersed with theory lesson that cover the GCSE exam content. The project finishes during the Summer term and students immediately then begin their GCSE non-exam assessment project that will account for 50% of their final overall GCSE grade. |
|
Year 11 Graphics, Resistant Materials and Textiles |
Students continue to work on their GCSE non-exam assessment project that will account for 50% of their final overall GCSE grade, the final hand-in deadline for which is in March. After this students concentrate on theory and exam paper content in the run up to the summer GCSE exam papers. |
Assessment Overview
KS3 –
In each subject that students study they are assessed on their practical outcomes and one of the following skills – Research, Designing, Analysing and Evaluating.
KS4 –
Students are assessed in line with the AQA exam board specification as detailed below.
Exam structure
Written exam Paper, 2hours – Marked out of 100 and worth 50% of GCSE award. Taken at the end of Year 11 and marked externally.
- Section A – Core technical principles (20 marks). A mixture of multiple choice and short questions assessing general Technology knowledge.
- Section B – Specialist technical principles (30 marks). Questions based around students selected specialism, several short answer question and one extended response to assess more in depth knowledge.
- Section C – Designing and making principles (50 marks). A mix of short and long answer questions.
Non-exam assessment, 30-35hours approx. Portfolio based design and make task, marked out of 100 and worth 50% of GCSE award. Marked by teachers then externally moderated by exam board, started at the end of Year 10 and assessed as follows –
- Identifying and investigating design possibilities (10 marks)

- Producing a design brief and specification (10 marks)

- Generating design ideas (20 marks)
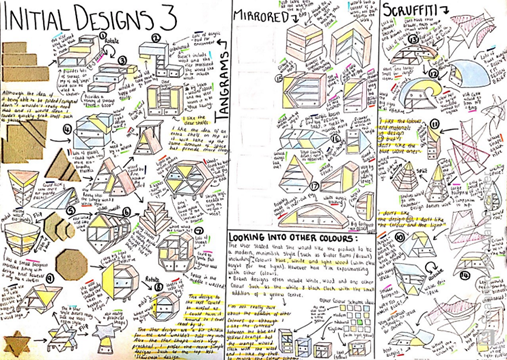
- Developing design ideas (20 marks)
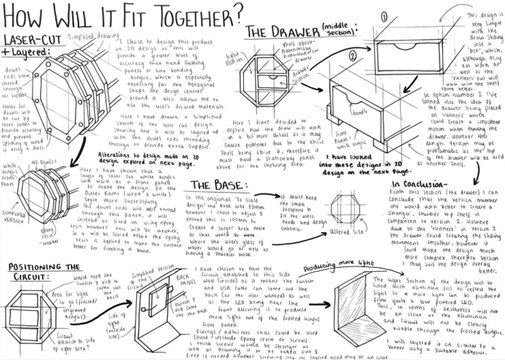
- Realising design ideas (making) (20 marks)

- Analysing and evaluating (20 marks)
How we build on prior knowledge
We find that students often arrive at SVCS with very little experience of Technology at KS2, particularly in terms of Resistant Materials and Graphics. Our projects are designed to introduce students to safe working practices in workshop, studio and food preparation environments, while also introducing them to the research, design and evaluation skills they will need to successful complete each project. Each project in the different subject areas builds on the theory and practical skills learnt the year before, either introducing totally new elements and techniques, or through the introduction of more advanced skills. As knowledge of research, design and evaluation as common themes for all Technology subjects students have the opportunity to re-visit build on this knowledge as they move through the different courses of the course of the year.
Cross-curricular with other subjects
- Maths – Measurement, proportion, data representation, use of vector-based CAD design programs. The GCSE exam has a maths content
- Science – Forces, Material properties, environmental and ecological considerations, electronics.
- English – Written evaluations and research.
- History – Historical context links to design movements.
- Computer Science – Use of CAD design programs, understanding of input/outputs.
- Geography – Environmental and ecological considerations.
- PE – Forces and movement.
- Art – Art and design movements and associated companies/products, importance of aesthetics in design, presentation of design work and drawing skills.
Enrichment opportunities
Extra-curricular Technology also provides a wide variety of opportunities for performing outside of lessons for those students who have a passion for the subject. We run a STEM club where we are currently building and electric powered car that once completed can be entered in a race series. For our KS4 students we run a trip to the Design Museum to aid them with the initial sections of their Non-exam assessment projects.
Useful resources to support learning
- https://www.pinterest.co.uk/SVCSTechDept/
- https://senecalearning.com/en-GB/
- https://technologystudent.com/
- https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/subjects/zvg4d2p
- AQA Design & Technology: Timber, Metal based materials and polymers; published by Hodder Education ISBN 9781510401129.
- AQA Design & Technology: Paper & boards; published by Hodder Education ISBN
- GCSE AQA design and Technology For the grade 9-1 course, The revision guide, published CGP. ISBN 9781782947523.
How can parents/carers support learning at home?
- Engaging with the world through the use of designed objects, discussing what objects in your home are well designed? How could object be improved to make them easier to use? How could object be re-designed to make them more accessible to a person with additional needs.
- Watching relevant Art and Design documentaries together such as ‘Abstract – The art of design’
- Watch documentaries on climate change, pollution and fair trade together and discuss what can be done to minimise these when designing, manufacturing and using products.
- Provide feedback on students designs. At KS4 students must have a ‘real’ client that they engage with throughout the design and making process.
- Visit Art and Design museum and exhibitions together such as – The Design Museum, The V&A, The Tate.
Studying Technology is useful if you are considering the following careers:
Engineering; product and industrial design; fabrications; Architecture; jewellery design; fashion and textiles design; film and theatre set design; self-employed craftspeople; graphic designer/artist; illustrator; cartoonist, animator; book and magazine design; web based design; and advertising.